 |
Bacteriophage: Category of viruses that infect bacterial cells.
 | |
Cloning: Making a genetically identical copy of DNA or of an organism.
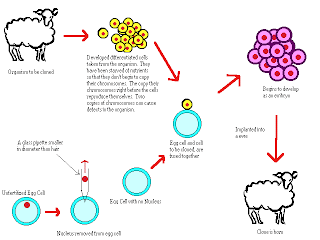 |
| Cloning |
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): Of cells and many viruses, the molecule of inheritance. H bonds join its two helically twisted nucleotide strands, one of which has instructions (in its base sequence) for synthesizing all of the enzymes and other proteins required to build and maintain cells.
DNA ligase: Enzyme that seals new base-pairings during DNA replication.
DNA polymerase: Enzyme of replication and repair that assembles a new strand of DNA on a parent DNA template.
DNA repair: Enzyme-mediated process that fixes small-scale alterations in a DNA strand by restoring the original base sequence.
DNA replication: Any process by which a cell duplicates its DNA molecules before dividing.
Guanine: Nitrogen-containing base in one of four nucleotide monomers of DNA or RNA.
Guanine: Nitrogen-containing base in one of four nucleotide monomers of DNA or RNA.
Nucleotide: Small organic compound with deoxyribose (a five-carbon sugar), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. Monomer for adenosine phosphates, nucleotide coenzymes, and nucleic acids.
Thymine: A nitrogen-containing base; one of the nucleotides in DNA (not in RNA).
X-ray diffraction image: Pattern that forms on film exposed to x-rays that have been directed at a molecule; reveals positions of atoms, not the molecular structure.
Anticodon: Series of three nucleotide bases in tRNA; can base-pair with an mRNA codon.
Base sequence: Sequential order of bases in a DNA or RNA strand.
Base-pair substitution: One amino acid has replaced another during protein synthesis.
Codon: One of 64 possible base triplets in an mRNA strand. A code word for an amino acid in a polypeptide chain; a few codons also act as START or STOP signals for translation.
Deletion: At cytological level, loss of a segment from a chromosome. At molecular level, loss of one to a few base pairs from a DNA molecule.
Gene mutation: A small-scale change in the nucleotide sequence of a DNA molecule.
Thymine: A nitrogen-containing base; one of the nucleotides in DNA (not in RNA).
X-ray diffraction image: Pattern that forms on film exposed to x-rays that have been directed at a molecule; reveals positions of atoms, not the molecular structure.
Anticodon: Series of three nucleotide bases in tRNA; can base-pair with an mRNA codon.
Base sequence: Sequential order of bases in a DNA or RNA strand.
Base-pair substitution: One amino acid has replaced another during protein synthesis.
Codon: One of 64 possible base triplets in an mRNA strand. A code word for an amino acid in a polypeptide chain; a few codons also act as START or STOP signals for translation.
Deletion: At cytological level, loss of a segment from a chromosome. At molecular level, loss of one to a few base pairs from a DNA molecule.
Exon: One of the base sequences of an mRNA transcript that will become translated.
Intron: A noncoding portion of a pre-mRNA transcript; excised before translation. Gene mutation: A small-scale change in the nucleotide sequence of a DNA molecule.
Genetic Code: The correspondence between nucleotide triplets in DNA (then mRNA) and specific sequences of amino acids in a polypeptide chain; the basic language of protein synthesis in cells.
Insertion: Insertion of one to a few bases into a DNA strand.
Ionizing Radiation: High-energy wavelengths.






















